Surveillance Systems: Transponders and ADS-B, The proliferation of technology in recent decades has seen rapid advancements in various surveillance systems that enhance safety, security, and efficiency across several industries. In the realm of aviation, this is evident in the form of transponders and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) systems. These technologies play a critical role in modern-day air traffic management, ensuring the safe and orderly movement of aircraft in the skies.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of both transponders and ADS-B, discussing their history, operation, significance, and the future prospects they hold for revolutionizing aviation safety and surveillance.
Surveillance Systems: Transponders and ADS-B
1. Transponders: An Overview
1.1 What are Transponders?
A transponder is an electronic device that, upon receiving a specific signal, responds by transmitting a predetermined message. In aviation, transponders are used primarily for aircraft identification and location purposes.
1.2 History of Transponders
The idea of a transponder originated during World War II, when they were used as Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) systems. These systems helped identify whether an incoming aircraft was an ally or an enemy.
Over time, the use of transponders evolved. By the 1950s and 1960s, commercial and civil aviation began to incorporate transponders for air traffic control (ATC) purposes.
1.3 How Transponders Work
In aviation, transponders work in tandem with ground-based radar. The radar sends an interrogation signal, and the transponder aboard the aircraft responds with specific information. This information typically includes an aircraft’s unique identification code and, in more advanced systems, altitude data.
1.4 Significance in Air Traffic Management
Transponders have proven essential in improving situational awareness for ATC. By providing precise aircraft location and identification details, controllers can efficiently manage multiple aircraft in dense airspace, reducing the risk of mid-air collisions.

2. ADS-B: The Future of Aviation Surveillance
2.1 What is ADS-B?
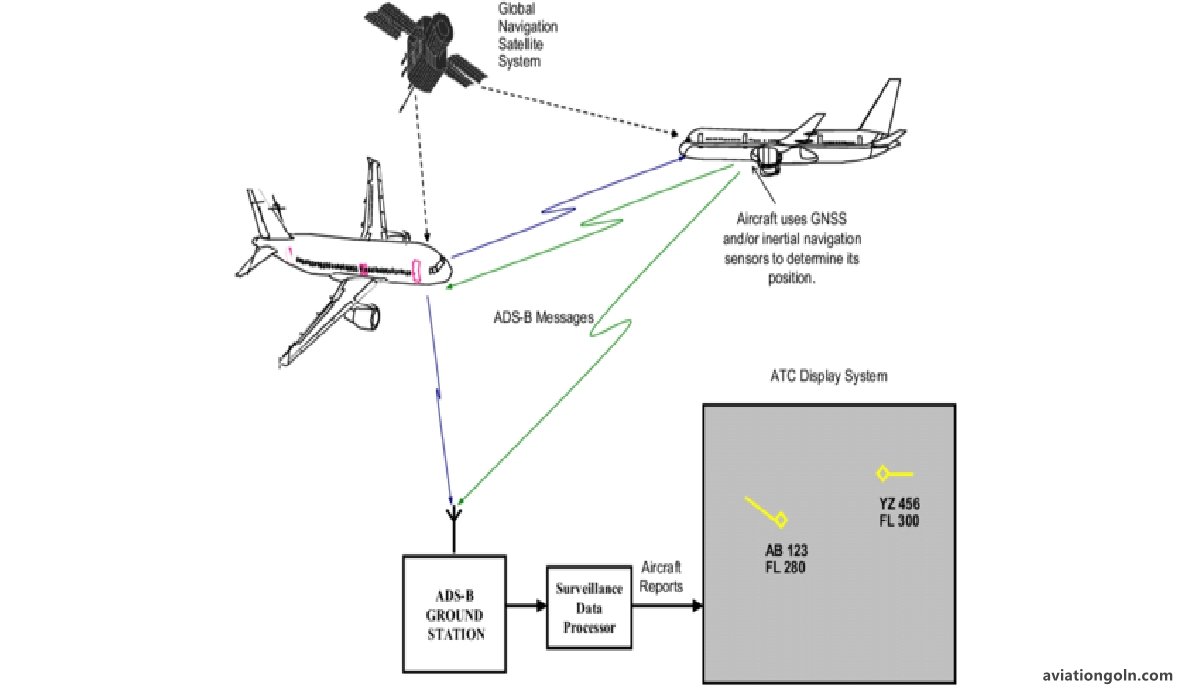
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) is a surveillance technology that allows aircraft to determine their position via satellite navigation. This position, along with other relevant data, is then broadcast for consumption by air traffic control and other nearby aircraft.
2.2 History and Development
The conceptual framework for ADS-B began to form in the 1990s as a potential solution to the limitations of traditional radar-based surveillance. Its full-scale implementation commenced in the early 21st century, with countries like the United States making it mandatory for most aircraft to be equipped with ADS-B Out capabilities by 2020.
2.3 How ADS-B Works
There are two main components to the ADS-B system:
- ADS-B Out: This component broadcasts information from the aircraft to ground stations and other nearby aircraft. The data includes identification, current position, altitude, speed, and direction.
- ADS-B In: This is the capability for an aircraft to receive ADS-B signals from other aircraft and ground stations. It provides pilots with a real-time display of air traffic in their vicinity.
Unlike traditional radar, ADS-B doesn’t rely on interrogations. Instead, aircraft automatically broadcast their information at regular intervals.

2.4 ADS-B vs. Traditional Transponders
There are distinct advantages of ADS-B over traditional transponder-based systems:
- Accuracy: ADS-B provides more accurate positioning due to its reliance on satellite navigation systems.
- Update Rate: While radar might update every few seconds, ADS-B information is broadcast almost continuously.
- Coverage: ADS-B has the potential for global coverage, especially with space-based ADS-B systems.
- Direct Aircraft-to-Aircraft Communication: ADS-B allows for direct communication between aircraft, aiding in situational awareness.
2.5 The Importance of ADS-B in Modern Air Traffic Management
With the growing volume of air traffic, the need for a more efficient surveillance system became evident. ADS-B addresses many limitations of radar and transponder systems:
- Enhanced Safety: Provides pilots with a clearer picture of nearby traffic.
- Increased Capacity: Can handle more aircraft simultaneously.
- Efficiency: Allows for more direct routing and flight paths.
- Cost-effective: Ground-based ADS-B stations are cheaper to install and maintain than radar systems.
3. Challenges and Considerations
While transponders and ADS-B have revolutionized aviation surveillance, they’re not without challenges:
- Security Concerns: Like all digital systems, ADS-B is susceptible to spoofing and hacking.
- Implementation Costs: For airlines, retrofitting older aircraft with ADS-B technology can be costly.
- Global Standardization: While many countries have adopted ADS-B, global harmonization of standards and procedures is still a work in progress.

4. The Future of Surveillance Systems in Aviation
The continuous evolution of technology promises a brighter future for aviation surveillance:
- Space-based ADS-B: Companies like Aireon are deploying satellites equipped with ADS-B receivers. This provides true global coverage, even over oceans and remote areas.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: AI could process vast amounts of data to predict traffic flow, potential conflicts, and suggest optimal routes.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: Efforts are underway to bolster the security aspects of ADS-B to prevent unauthorized access and tampering.

From the rudimentary IFF systems of World War II to the sophisticated ADS-B systems of today, aviation surveillance has come a long way. The overarching goal remains the same: ensuring the safety and efficiency of air traffic. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the tools and systems that keep our skies safe. Transponders laid the groundwork, and ADS-B is taking the baton forward, heralding a new era of enhanced situational awareness and global coverage in air traffic management.
Read more:
