Certification Standards and Procedures: Flight testing and certification are critical processes in the aviation industry. Before any new aircraft or significant modification to an existing one, is allowed to enter service and carry passengers, it must undergo rigorous testing and be certified by appropriate regulatory agencies. This ensures that the aircraft is safe, reliable, and meets strict performance standards.
Certification Standards and Procedures
This article provides an in-depth understanding of the certification standards and procedures involved in flight testing and the final certification of aircraft.
1. Overview of Flight Testing
Flight testing is a structured process of evaluating an aircraft’s performance, handling, and systems under various operating conditions.
1.1 Types of Flight Testing
- Developmental Testing: Conducted during the aircraft design and development phase to verify the aircraft’s performance against design objectives.
- Certification Testing: Performed to demonstrate that the aircraft complies with regulatory standards and can safely operate in its intended environment.
- Operational Testing: Carried out by operators (like airlines) to assess how the aircraft fits into their operational environment.
1.2 Objectives of Flight Testing
- Safety Verification: Ensuring that the aircraft can be flown safely under all anticipated operational conditions.
- Performance Evaluation: Determining the aircraft’s speed, range, altitude, and other performance metrics.
- Systems Assessment: Verifying the correct functioning of all aircraft systems, including avionics, fuel, and navigation systems.

2. Certification Standards
The primary goal of certification is to ensure the safety of air transportation. The process involves verifying that an aircraft complies with all established standards and regulations.
2.1 The Role of Regulatory Agencies
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA): In the U.S., the FAA oversees the certification of all civilian aircraft. They have established the Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs) to set the standards for aircraft design, construction, and operation.
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA): For Europe, EASA is responsible for civil aviation certification, setting its standards through European Aviation Safety Regulations.
- Other National Authorities: Many countries have their aviation regulatory bodies, like Transport Canada or the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC).
2.2 Key Certification Standards
Certification standards cover various aspects of aircraft design and operation:
- Airworthiness Standards: These dictate the minimum requirements an aircraft must meet to be considered safe for operation. They cover structural integrity, system reliability, and more.
- Operational Standards: These focus on the actual operation of the aircraft, such as crew training requirements, maintenance procedures, and operating limits.
- Environmental Standards: These ensure that the aircraft meets noise and emissions standards.
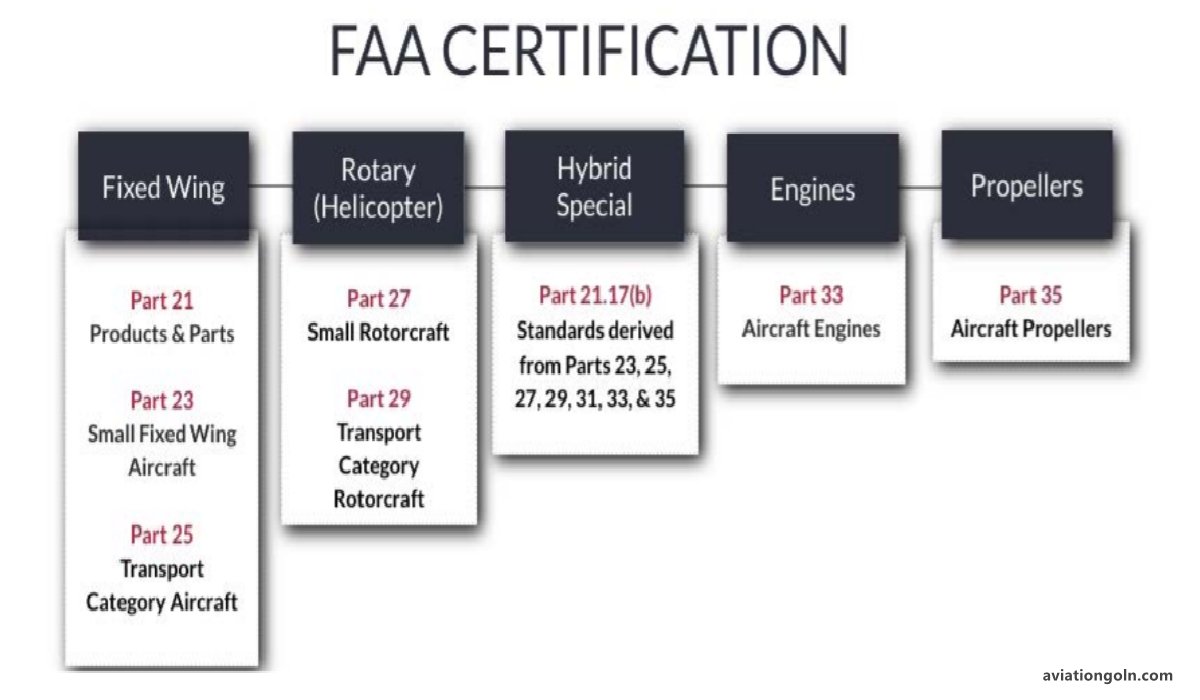
3. The Certification Process
The path to certification involves several steps:
3.1 Pre-application Phase
Before a formal application is made, there are discussions between the aircraft manufacturer and the regulatory body. This ensures that both parties have a clear understanding of the certification requirements and process.
3.2 Formal Application
Once the manufacturer is ready, they submit a formal application to the regulatory body, outlining the aircraft’s design, intended operations, and how it meets the certification standards.
3.3 Document Evaluation
The regulatory body reviews all provided documentation to ensure it’s complete and meets the defined criteria.
3.4 Ground and Flight Testing
The most hands-on phase, this involves extensive testing:
- Ground Testing: Tests systems while the aircraft is on the ground. This can involve static tests, where the aircraft is subjected to loads and stresses, and systems tests, where the aircraft’s systems are operated and evaluated.
- Flight Testing: Involves actually flying the aircraft under various conditions to validate its performance, handling, and safety.

3.5 Conformity Inspection
The regulatory body will inspect the aircraft to ensure that it has been built to the approved design and that no unapproved changes have been made.
3.6 Type Certificate Issuance
If the aircraft successfully meets all requirements, the regulatory body issues a Type Certificate, indicating that the aircraft design is certified for production and operation.
3.7 Production and Airworthiness Certification
Even after the design is certified, each individual aircraft produced must receive an Airworthiness Certificate, ensuring it was manufactured and maintained according to the certified design.
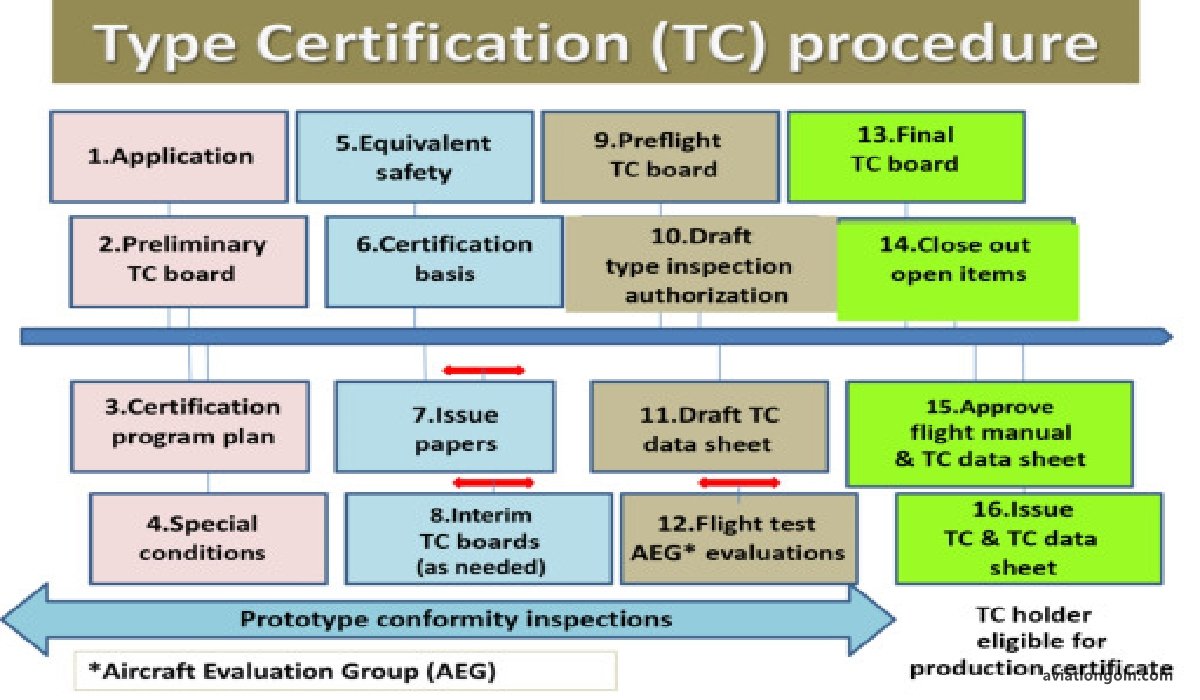
4. Challenges and Considerations in Flight Testing and Certification
The path to certification is not always straightforward:
- Changes in Standards: As technology and understanding evolve, so do certification standards. An aircraft in development may need to adapt to new or updated regulations.
- Global Certification: For aircraft intended for international markets, manufacturers may need to achieve certification from multiple regulatory bodies.
- Unanticipated Issues: Flight testing can reveal unexpected issues or behaviors that require design changes, leading to delays and additional costs.
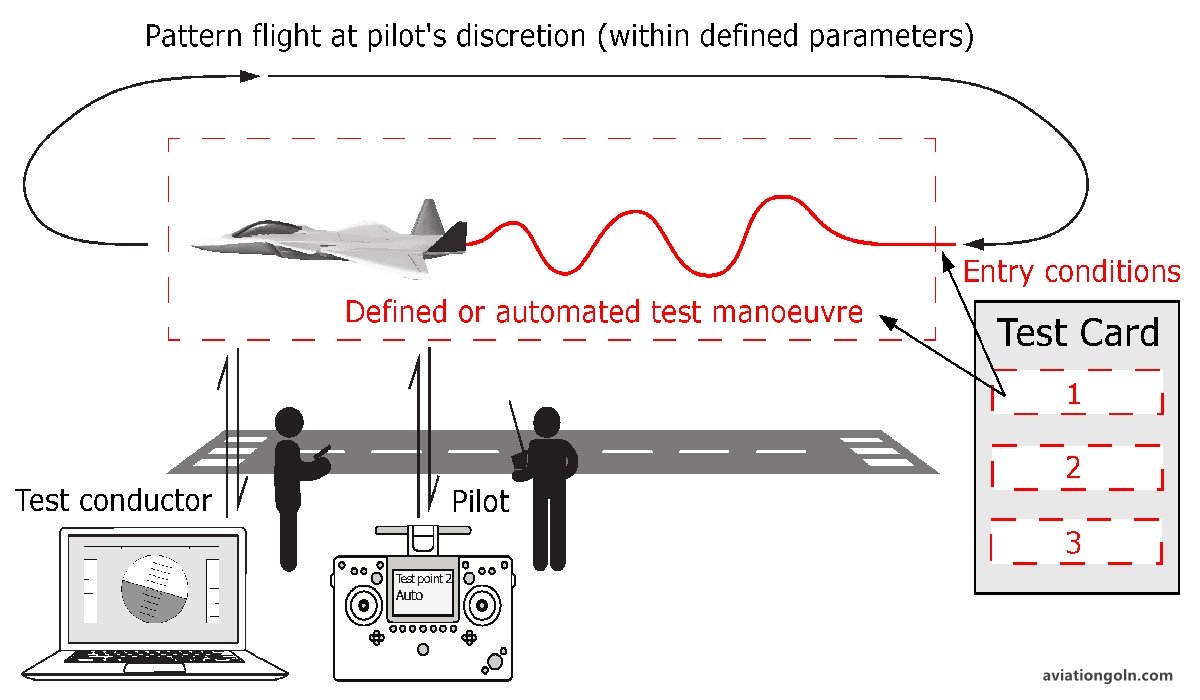
Flight testing and certification are fundamental processes that ensure the safety and reliability of aircraft. By adhering to strict standards and undergoing rigorous evaluations, manufacturers and regulatory bodies work together to ensure that every aircraft flying in the skies is as safe as possible. As aviation technology continues to advance, these processes will adapt, but their core objective—ensuring the safety of all passengers and crew—will remain unchanged.
