In the ever-evolving world of avionics, one thing remains constant: the need for reliable communication between various aircraft systems. As aircraft become more complex and the demand for better, faster, and more efficient data communication increases, the role of avionics data buses and networking becomes ever more crucial. This article dives deep into the intricacies of data buses and networking in the realm of avionics hardware, shedding light on their history, architecture, operation, and significance in modern aviation.
Data Buses and Networking in Avionics: Avionics Hardware
What is a Data Bus?
In simple terms, a data bus is a communication system that transfers data between components within an aircraft or between the aircraft and external equipment. The data bus serves as the “highway” upon which all communication traffic travels. It’s integral to the proper functioning of aircraft systems, sensors, and avionics suites.

Historical Overview
The initial aircraft systems were rudimentary and didn’t require sophisticated communication channels. However, as avionics systems began to incorporate more advanced electronics, the need for a structured communication network became evident.
The first-generation avionics buses, which emerged in the 1970s, were simple serial interfaces. The ARINC 429, introduced in the late 70s, became the de facto standard for data bus communication in commercial aircraft. Since then, the evolution of avionic data buses has progressed rapidly, leading to the development of more advanced bus systems, like MIL-STD-1553, ARINC 629, and ARINC 664.
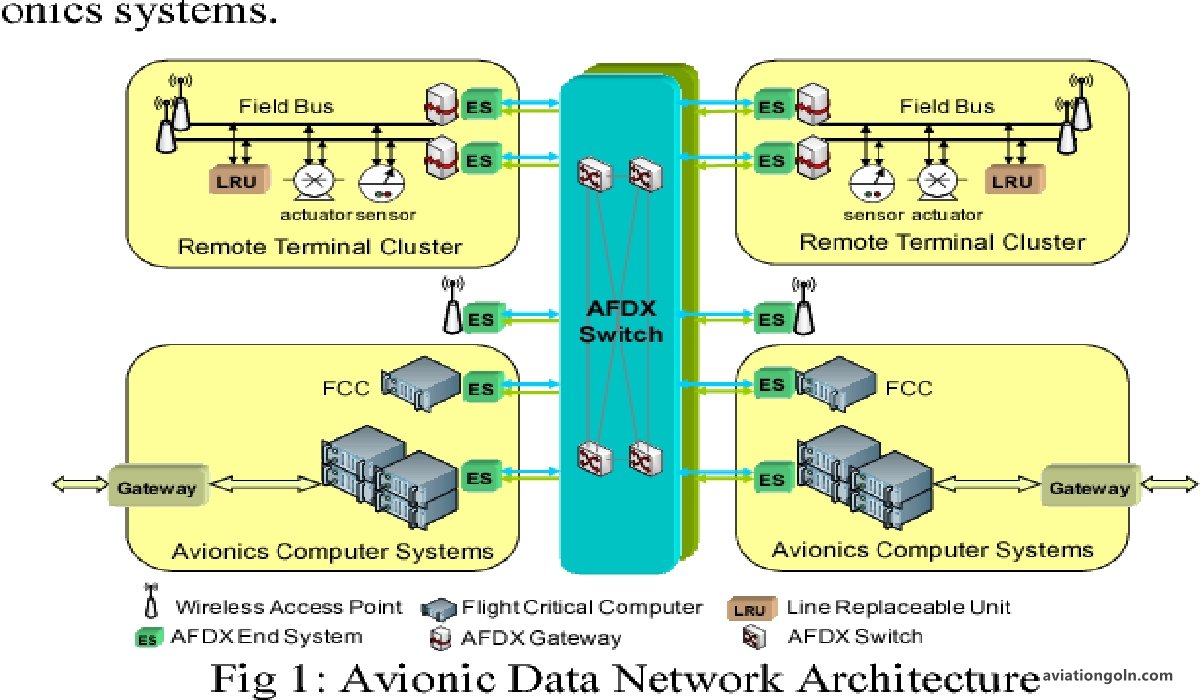
Key Avionic Data Buses
ARINC 429
Characteristics:
- Serial data bus
- Point-to-point topology
- Data rate of 100 kbps
ARINC 429 is a widely used data bus standard in both commercial and military aircraft. It utilizes a simple point-to-point connection, with one transmitter sending data to up to 20 receivers. This simplicity made it an ideal choice for early avionic systems.

MIL-STD-1553
Characteristics:
- Half-duplex serial data bus
- Uses tri-state logic
- Command/Response protocol
- Data rate of 1 Mbps

MIL-STD-1553 was designed for military applications and is predominantly found in military aircraft. It incorporates redundancy, with two physical bus channels (Bus A and Bus B). This bus operates in a command/response mode where the bus controller initiates commands, and remote terminals respond.

ARINC 629
Characteristics:
- Multi-transmitter data bus
- Used in Boeing 777 aircraft
- Data rate of 2 Mbps
As an improvement to ARINC 429, ARINC 629 allows multiple transmitters to communicate on the same physical bus. This bus system was adopted by the Boeing 777 aircraft and can handle a vast amount of data, making it suitable for modern avionic systems.

ARINC 664 (AFDX)
Characteristics:
- Ethernet-based network
- Used in Airbus A380, A350, and Boeing 787
- Data rate up to 100 Mbps
ARINC 664 or Avionics Full-Duplex Switched Ethernet (AFDX) is an advanced data network developed for modern avionic systems. It takes advantage of Ethernet technology, with modifications to meet the stringent requirements of avionics.

Networking in Avionics
While data buses allow for inter-component communication, networking is essential for the broader data communication structure in avionics. As aircraft incorporate more sophisticated systems, there’s a pressing need for a more structured networking approach.
Switching vs. Routing
In the context of avionics, switching refers to the process of directing data packets within a network based on MAC addresses. In contrast, routing directs data packets based on IP addresses. Modern avionic systems, especially those that incorporate ARINC 664, often use switches due to their speed and deterministic behavior.
Quality of Service (QoS)
In avionic networks, not all data is created equal. Some data, like flight control commands, is critical and requires priority over other non-essential data. QoS mechanisms in avionic networks ensure that vital data gets the highest priority, ensuring timely delivery and system stability.
Determinism
One of the most critical requirements in avionic systems is determinism. Deterministic systems ensure that specific operations completed in a fixed amount of time, every time. Given the safety-critical nature of avionics, having deterministic behavior, especially in data communication, is paramount.

Importance of Data Buses and Networking in Avionics
- Safety: Reliable communication ensures that flight-critical data is exchanged without error, ensuring the safe operation of the aircraft.
- Efficiency: A structured data communication system allows for quick decision-making, optimal system operation, and real-time monitoring.
- Scalability: Modern avionic systems are designed with scalability in mind. With the right data bus and network architecture, adding new systems or upgrading existing ones becomes straightforward.
- Data Integrity: Proper data communication ensures that data integrity is maintained. Any loss or alteration of data can have catastrophic consequences in an aviation context.
- Real-time Monitoring: For the crew and ground personnel, real-time data from the aircraft’s systems can be invaluable. It allows for quick responses to emerging situations and efficient maintenance.

As aircraft continue to evolve, the underlying avionics hardware, especially data buses and networks, must keep pace. These systems are the backbone of modern aircraft, ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable operations. Whether it’s the tried-and-tested ARINC 429 or the advanced ARINC 664, the role of data buses in avionics is undeniable. As we move towards more integrated and intelligent aircraft, the world of avionic data communication is bound to see even more advancements, holding promise for an exciting future in aviation technology.
