Components of an Aircraft Engine: Aircraft engines are intricate machines designed to convert fuel into mechanical energy to propel an aircraft through the air. They are a testimony to human innovation and have gone through extensive advancements over the past century. This article delves deep into the components that constitute these marvels of engineering.
Components of an Aircraft Engine
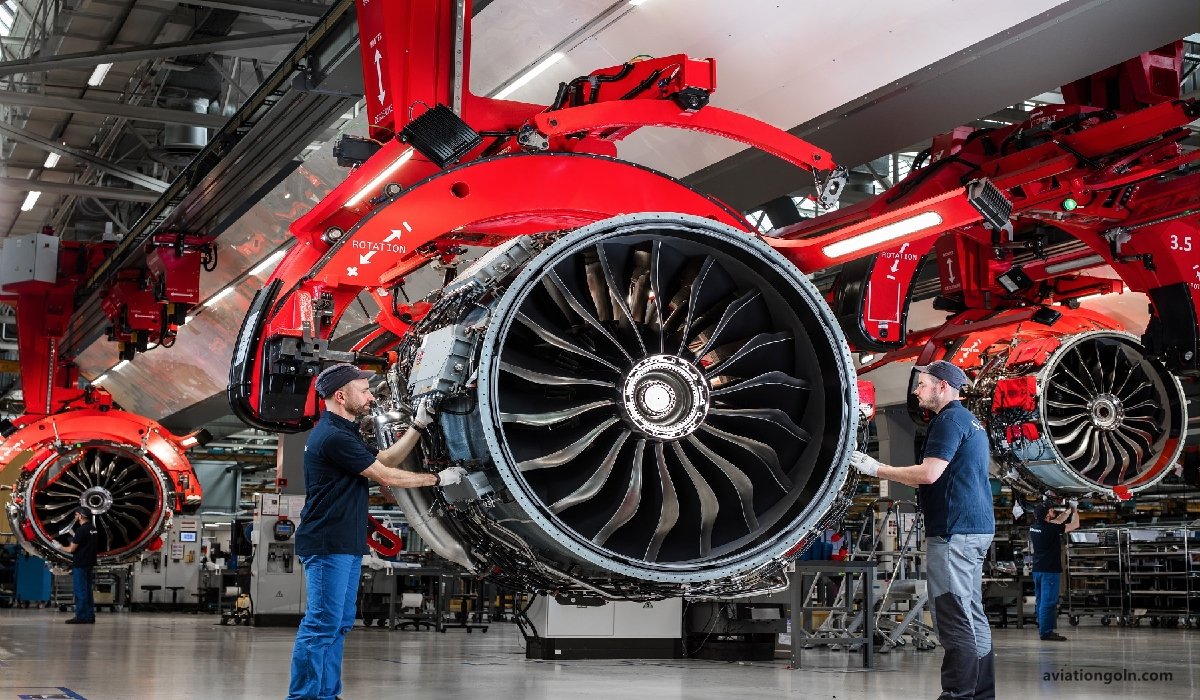

Introduction
The aircraft engine, irrespective of its type, is a complex assembly of numerous parts, each serving a unique purpose. Each component is meticulously designed and manufactured to withstand the rigors of flight, ensuring safety, performance, and reliability.

Key Components of an Aircraft Engine
1. Intake
Before diving into the internal components, it’s essential to understand the intake system. The intake is designed to direct incoming air into the engine. For jet engines, this intake must efficiently compress the incoming air, especially at high speeds, to optimize performance.

2. Compressor
Once air enters the engine, it must be compressed before combustion. The compressor plays this vital role. There are primarily two types of compressors:
- Axial Compressor: Consists of multiple stages of rotor and stator blades. The air flows parallel to the axis of rotation, getting compressed as it passes through each stage.
- Centrifugal Compressor: Uses an impeller to accelerate the air outward. A diffuser then slows this air down, increasing its pressure.

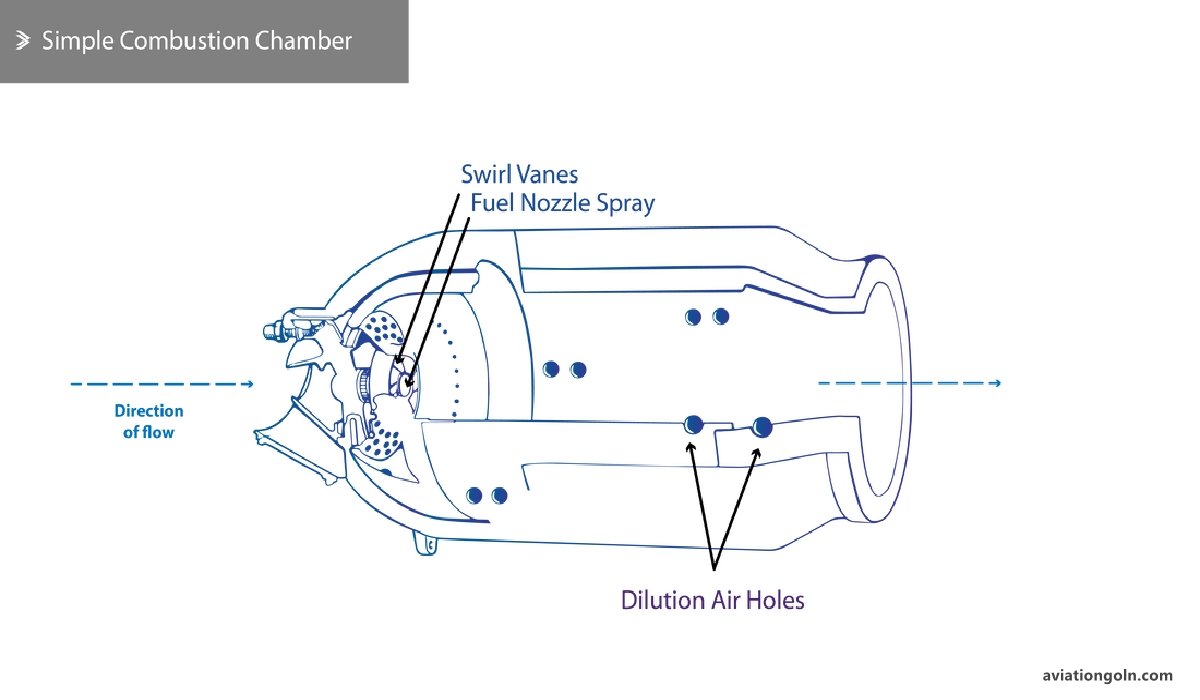
3. Combustion Chamber
This is where the magic happens. The high-pressure air from the compressor is mixed with fuel and then ignited. The combustion chamber ensures efficient and continuous burning of the fuel-air mixture. There are several types of combustion chambers, including:
- Can Type: Individual combustion chambers for each cylinder.
- Annular Type: A continuous ring-shaped combustion space.
- Can-Annular Type: A combination of can and annular designs.
4. Turbine
Post-combustion, the high-energy exhaust gases flow over the turbine blades, causing them to rotate. The turbine captures energy from these gases to drive the compressor and other engine accessories. The turbine’s design and material must withstand high temperatures and pressures.

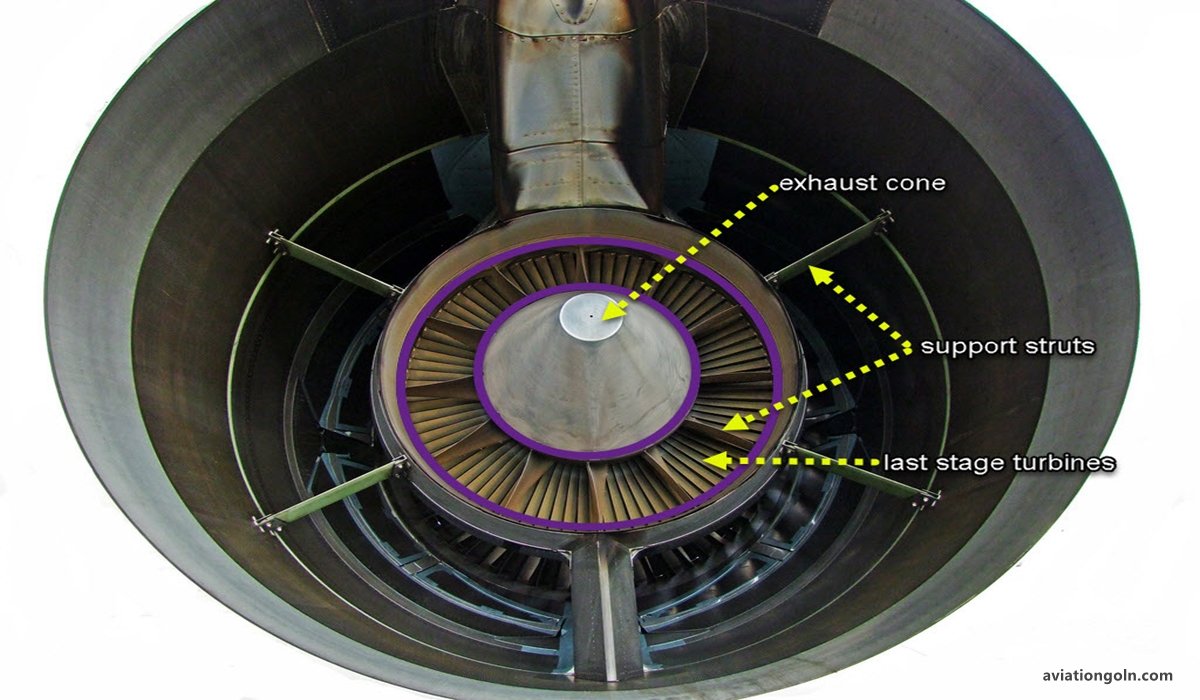
5. Exhaust Nozzle
The exhaust nozzle is the engine’s exit point. It’s designed to expel gases at high speeds, producing thrust according to Newton’s third law of motion. The shape and size of the nozzle play a pivotal role in determining the velocity of these exhaust gases.
6. Fan
Predominantly found in turbofan engines, the fan is located at the front. It draws in massive volumes of air, with a significant portion bypassing the core engine. This bypassed air produces additional thrust, making turbofans more efficient for commercial airliners.

7. Gearbox
Especially in turboprop engines, a gearbox is essential. It adjusts the high rotational speeds of the turbine to the optimal speeds for the propeller.
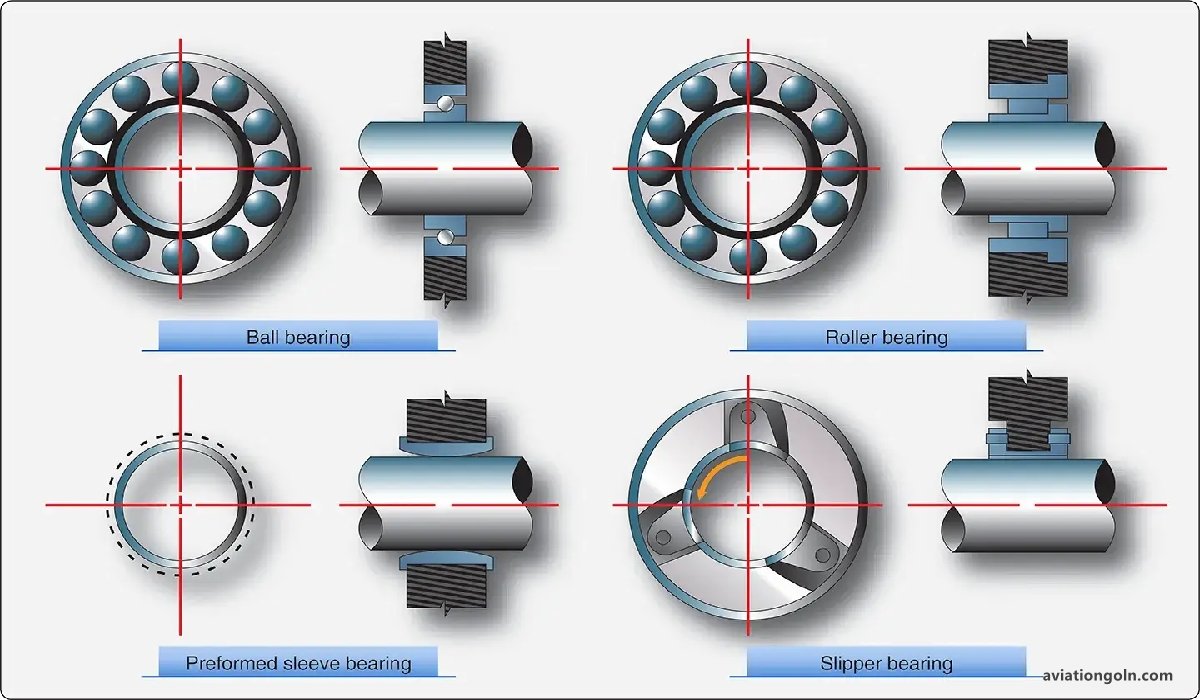
8. Bearings and Seals
Bearings support the rotating components like the shaft connecting the turbine and compressor. Seals, on the other hand, prevent oil leakage and ensure that air and oil do not mix.
9. Fuel System
The fuel system comprises fuel pumps, filters, and injectors or atomizers. It ensures that the right quantity of fuel is delivered to the combustion chamber under all operational conditions.

10. Ignition System
Similar to a car’s spark plug, the ignition system provides the initial spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. Once the engine is running, the continuous combustion ensures the engine remains ignited.
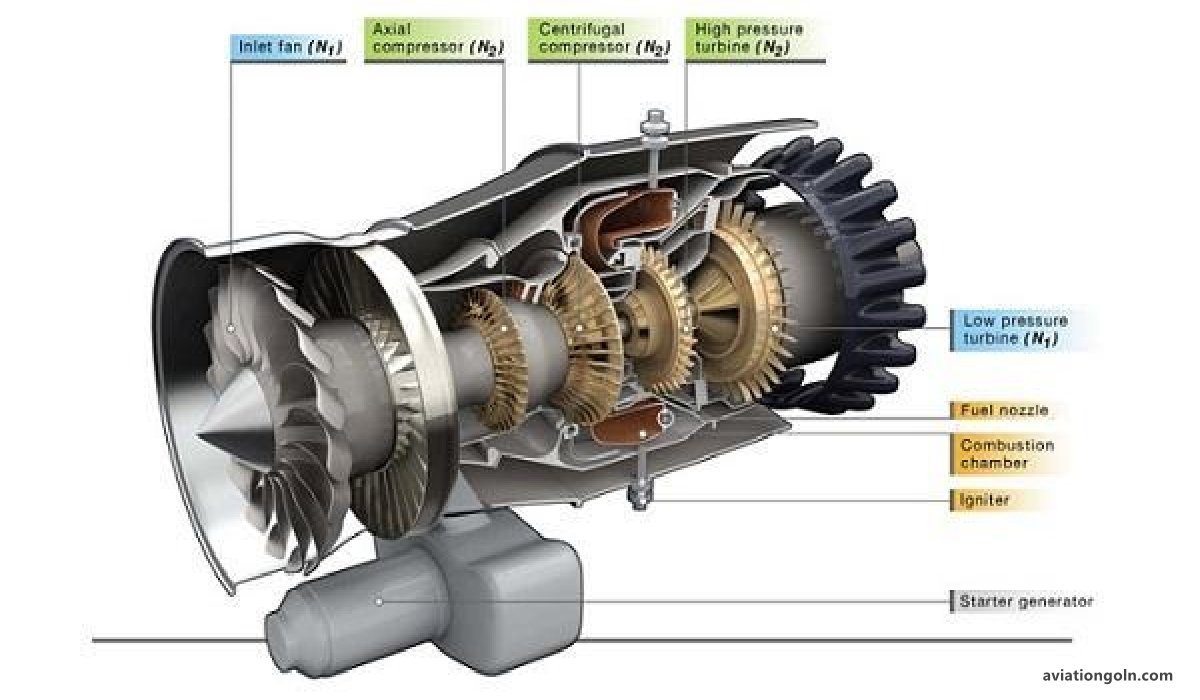
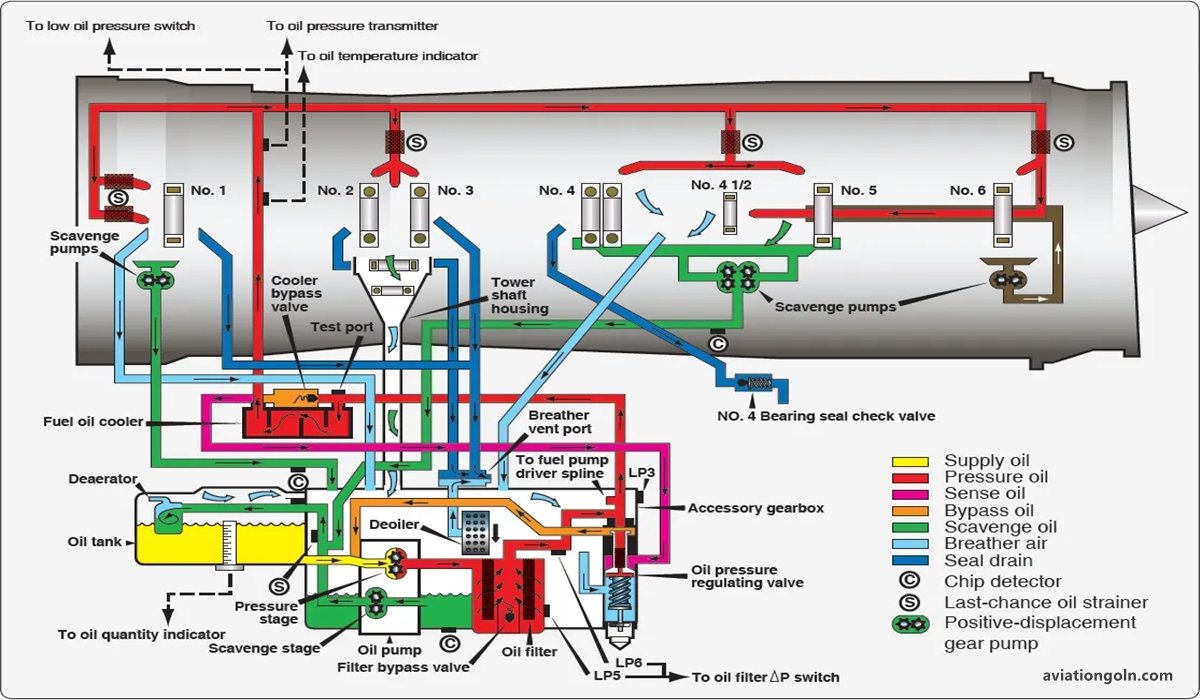
11. Lubrication System
An aircraft engine comprises numerous moving parts, and to reduce wear and tear, a lubrication system is vital. It distributes oil to various engine components, reducing friction and dissipating heat.
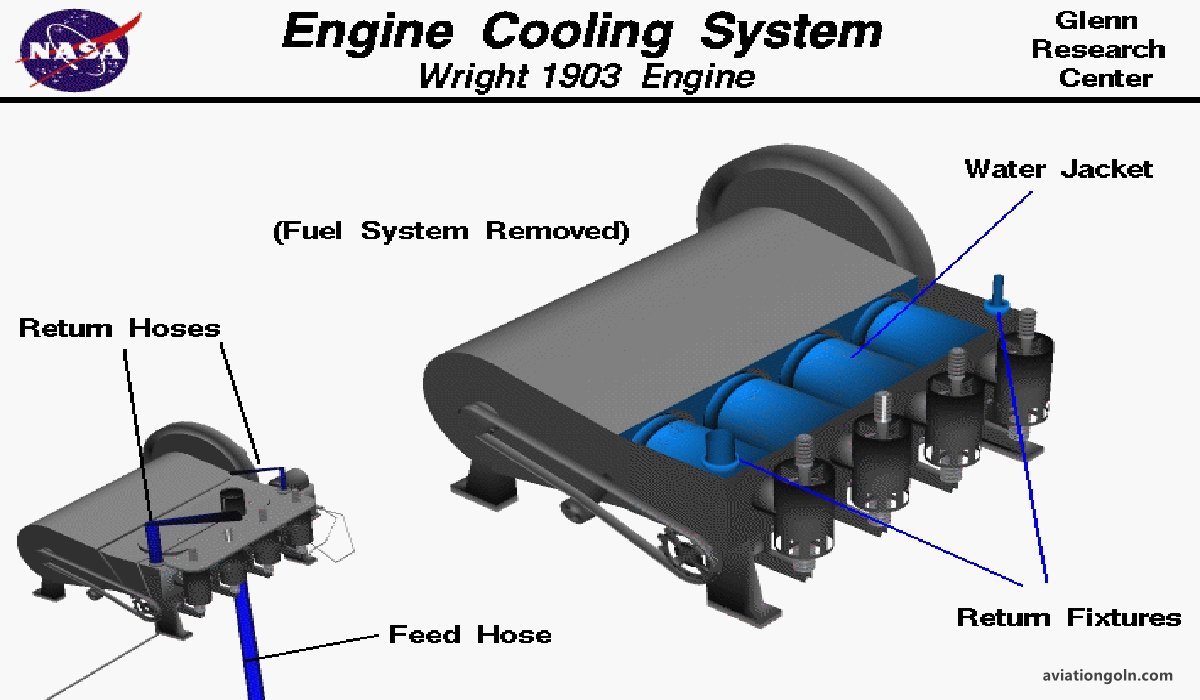
12. Cooling System
Overheating can be detrimental to an engine’s performance and lifespan. The cooling system, whether it uses air or liquid, ensures that the engine operates within a safe temperature range.
13. Engine Controls
This is the interface between the pilot and the engine. Engine controls allow the pilot to regulate power output, monitor engine health, and respond to any malfunctions.

Advancements in Engine Components
Aircraft engine components have seen significant advancements over the years:
- Materials: Modern engines use advanced materials like composites and ceramics. These materials can withstand higher temperatures, reducing the need for cooling and improving overall efficiency.

- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): Engineers now use CFD to optimize the design of components, ensuring efficient airflow, reduced drag, and improved combustion.
- Digital Controls: Gone are the days of purely mechanical controls. Modern engines use Full Authority Digital Engine Controls (FADEC) for precise control and optimal performance.

Maintenance and Importance of Quality Components
Given the extreme conditions under which aircraft engines operate, regular maintenance is crucial. Components wear out and must be inspected, repaired, or replaced to ensure the engine’s reliability and safety.
Using quality components during manufacturing and maintenance is paramount. The aviation industry follows strict standards, with parts often requiring certifications to be used in an engine. This rigorous approach ensures that the engine performs optimally throughout its service life.
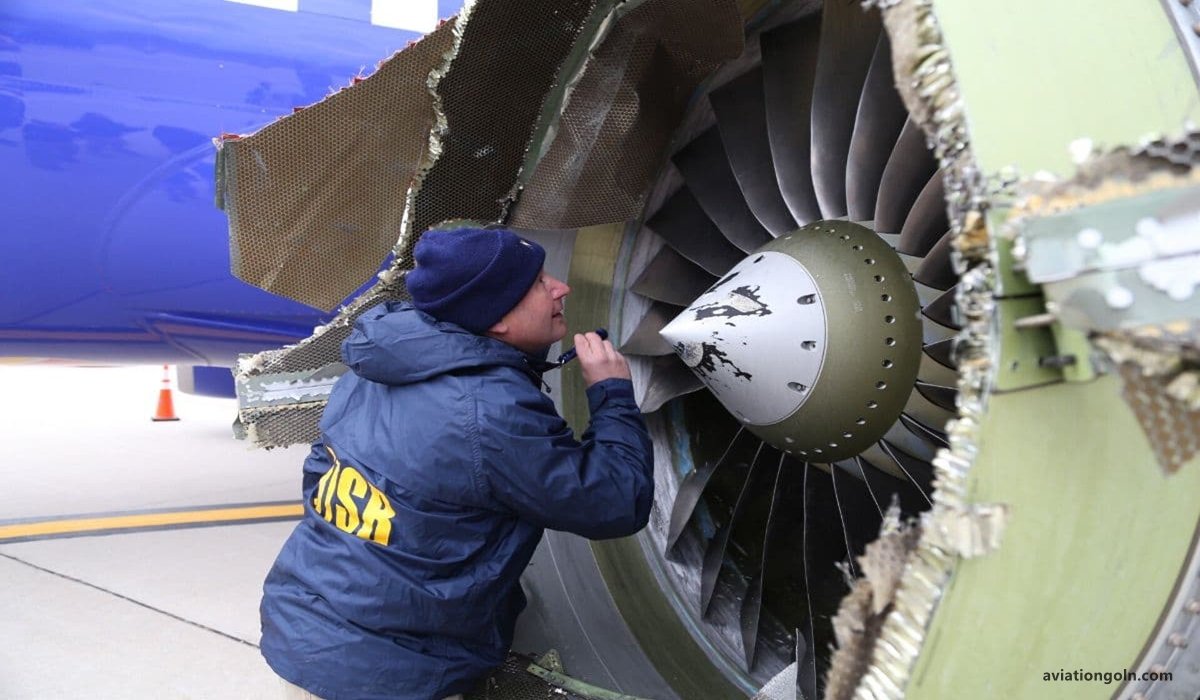

The aircraft engine, often described as the heart of an aircraft, is a symphony of components working in harmony. Each part, from the tiniest bearing to the massive fan blades, plays a critical role in achieving the marvel of flight. Understanding these components and their functions is not just essential for aviation professionals but offers anyone a deeper appreciation for the complexities and wonders of modern air travel.
Read more:
