English Language Proficiency Requirements

English Language Proficiency Requirements
Description
This article outlines standards and recommended practices, as of early 2021, for aircraft pilots and air traffic controllers to attain one of three recognized levels of English language proficiency (ELP). In many cases, specific language proficiency is required to comply with license qualifications.
The article focuses on relevant International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) standards and recommended practices and the European Union’s ELP adoption decisions.
Standardization of ELP requirements mitigates known risks of accidents in many types of flight operations, including business aviation and commercial air transportation between nations or regions.
Benefits from standard-setting include fully understood communications between pilots and controllers, despite distracting non-standard words and phrases.
High-level proficiency also enhances situational awareness through controller interactions and monitoring of surrounding air traffic communications.
Background
For 70 years, ICAO has analyzed risks involving linguistic issues, raised awareness of systemic risks, and pursued mitigations. From 2011–to 2021, ICAO and other stakeholders began to refine first-generation ELP standards and recommended practices.
ICAO set its first deadline — March 2008 — for the ICAO Member States, planning for ELP standards to take effect at Level 4, Level 5, or Level 6 for all pilots flying international routes and all air traffic controllers serving international airports and routes.
States unable to meet the first deadline were granted time to implement the acceptable language proficiency levels by March 2011. By 2013, ICAO reported that some Member States had serious difficulty and called on other nations to assist them.
ELP involves both native and non-native English speakers. According to ICAO, the burden for improving this aspect of aeronautical communications should not be seen as falling solely upon non-native English speakers.
Its Manual on the Implementation of ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements (Doc 9835), states: “Native speakers of English, too, have a fundamentally important role to play in the international efforts to increase communication safety.”
The following bullet points list basic concepts and expectations from FCL.055 Language Proficiency, a source frequently referenced by ICAO, EU, and UK CAA requirements:
- Airplane, helicopter, powered-lift and airship pilots required to use the radio telephony shall not exercise the privileges of their licenses and ratings unless they have a language proficiency endorsement on their license in either English or the language used for radio communications involved in the flight. The endorsement shall indicate the language, the proficiency level, and the validity date.
- The applicant for a language proficiency endorsement shall demonstrate, by Appendix 2 … at least an operational level of language proficiency both in the use of phraseologies and plain language.
- At the operational level, the applicant shall demonstrate the ability to:
- Communicate effectively in voice-only and in face-to-face situations;
- Communicate on common and work-related topics with accuracy and clarity;
- Use appropriate communicative strategies to exchange messages and to recognize and resolve misunderstandings in a general or work-related context;
- Handle successfully the linguistic challenges presented by a complication or unexpected turn of events that occur within the context of a routine work situation or communicative task with which they are otherwise familiar; and,
- Use a dialect or accent which is intelligible to the aeronautical community.
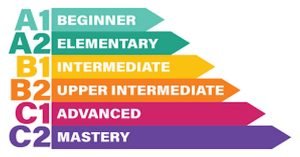
- Intervals for reevaluation of a pilot’s language-proficiency license endorsement depend on the pilot’s date of endorsement for demonstrating Level 4 (Operational Level), Level 5 (Extended Level), or Level 6 (Expert Level) proficiency, as follows:
- Four years, if the level demonstrated is operational;
- Six years, if the level demonstrated is extended level; and,
- Formal evaluation is not required for applicants who demonstrate expert level (i.e., native and very proficient non-native speakers with a dialect or accent intelligible to the international aeronautical community).
- Holders of an instrument rating, in addition to abilities noted, shall have demonstrated — by the competent authority’s method of assessment — their ability to use the English language at a level that allows them to:
- Understand all the information relevant to the accomplishment of all phases of a flight, including flight preparation;
- Use radiotelephony in all phases of flight, including emergencies; and,
- Communicate with other crew members during all phases of flight, including flight preparation.
International Standards
The current requirements for ELP license endorsement of operational personnel primarily are detailed in ICAO Annex 1 — Personnel Licensing and explained in Manual on the Implementation of ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements, ICAO Doc 9835 (see References).
Annex 1, 1.2.9, “Language Proficiency” (July 2018) includes the following selected facts about the applicability of ELP to specific aviation professions:
- “As of 3 November, 2022, airplane, airship, helicopter and powered-lift pilots; airplane, airship, glider, rotorcraft, powered-lift or free balloon remote pilots; air traffic controllers; and aeronautical station operators shall demonstrate the ability to speak and understand the language used for radiotelephony communications to the level specified in the language proficiency requirements in [Appendix 1, Requirements for Proficiency in Languages Used for Radiotelephony Communications].
- ”As of 3 November 2022, the language proficiency of airplane, airship, helicopter, and powered-lift pilots; airplane, airship, glider, rotorcraft, powered-lift or free balloon remote pilots; air traffic controllers; and aeronautical station operators who demonstrate proficiency below the Expert Level (Level 6) shall be formally evaluated at intervals by an individual’s demonstrated proficiency level.
- “Note: The provisions of 1.2.9 refer to Annex 10, Volume II, Chapter 5, whereby the language used for radiotelephony communications may be the language normally used by the station on the ground or English. In practice, therefore, there will be situations whereby flight crew members will only need to speak the language normally used by the station on the ground.”
Reassessment Procedures
As noted above, ICAO requires that the language skills of pilots and controllers rated at Level 4 are reassessed every three years, Level 5 pilots and controllers – every six years, while at Level 6, no further assessment of English language skills is deemed necessary.
Level 4 (operational) proficiency is considered as a minimum ‘stepping stone’ to higher levels. The main benefit of high international standards of aviation English is that communications between aircraft crew and controllers are fully understood, particularly when non-standard words and phrases are used. Also, improved language skills could help increase the situational awareness of flight crews about other aircraft, both in the air and on the ground.
Note: Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/340 states that the validity of the language proficiency endorsement for expert level (level six) is nine years from the date of assessment, for the English language. This provision is applicable to air traffic controllers in the EU member states.
Accidents and Incidents
The following events include “Language Clarity” as a contributory factor:

References
- Annex 1 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation – Personnel Licensing (see 1.2.9 Language Proficiency and Appendix A – Language Proficiency Rating Scale)
- Annex 10 – Aeronautical Communications, Volume II
- ICAO Doc 9835 AN/453 — Manual on the Implementation of ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements, Second Edition 2010.
- Rated Speech Samples Developed for ICAO by the International Civil Aviation English Association (ICAEA), an ICAO website accessed 28 March 2021.
- ICAO Language Proficiency Requirements, “Implementation and Maintenance Recommended Check-List,” updated on 13 March 2013.
- European Commission. “FCL.055 Language Proficiency” (with consolidated changes in force as of 12 January 2021). In Commission Regulation (EU) No 1178/2011 of 3 November 2011.
Related Articles
- AGE
- Language;
- Non-Standard Phraseology
- Standard Phraseology
- Message Format and Content
- Human Factors in AGC
- English Language Proficiency for Aeronautical Communication (ELPAC)
- AGC A&SI
- Accidents and Serious Incidents Reports: Air-Ground Communication;
Further Reading

ICAO
- Attachment A to State letter AN 12/44.6-07/68, Resolution A36-11 – Proficiency in the English language for Radiotelephony;
- Attachment B to State letter AN 12/44.6-07/68, Guidelines for the Development of a Language Proficiency Implementation Plan;
- ICAO Language proficiency requirements – Implementation and maintenance recommended check-list, updated on 13/03/2013;
- ICAO Circular 323 Guidelines for Aviation English Training Programmes – guidelines based on the work of the Board and members of the International Civil Aviation English Association (ICAEA);
- For more information on the ICAO, Language Proficiency Requirements consult the ICAO FSIX website: Implementation of Language Proficiency Requirements.
UK CAA
- Guidance for Examiners and Candidates: Process for the Testing of English Language, Standards Document No. 51, version 1.
